Understanding SCADA Systems and Their Importance
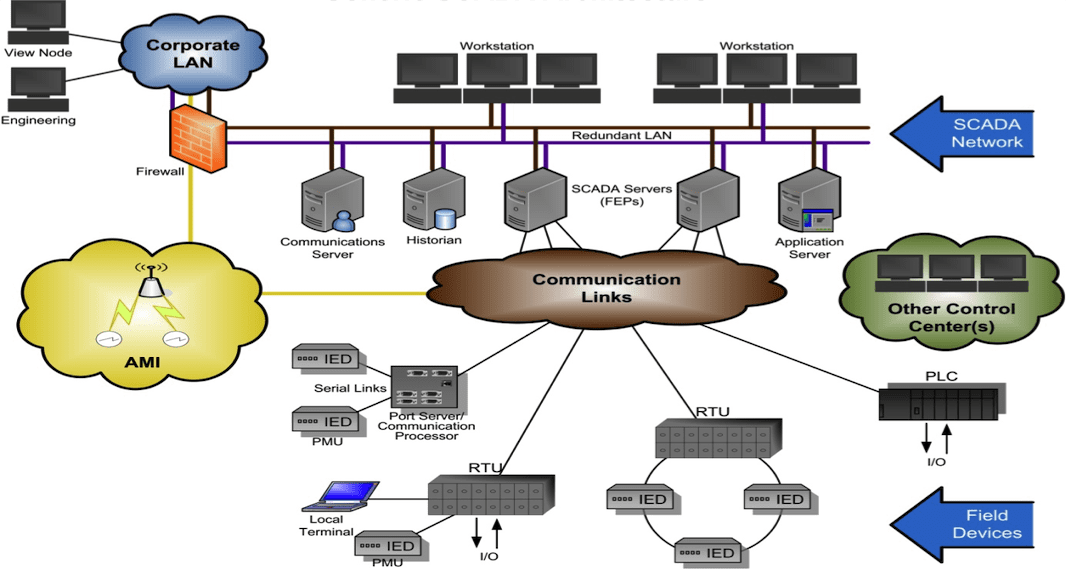
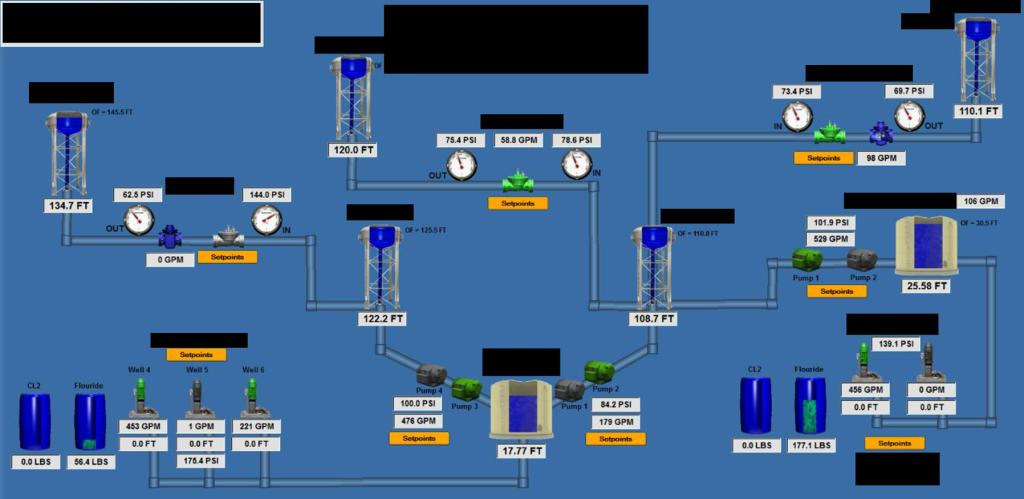
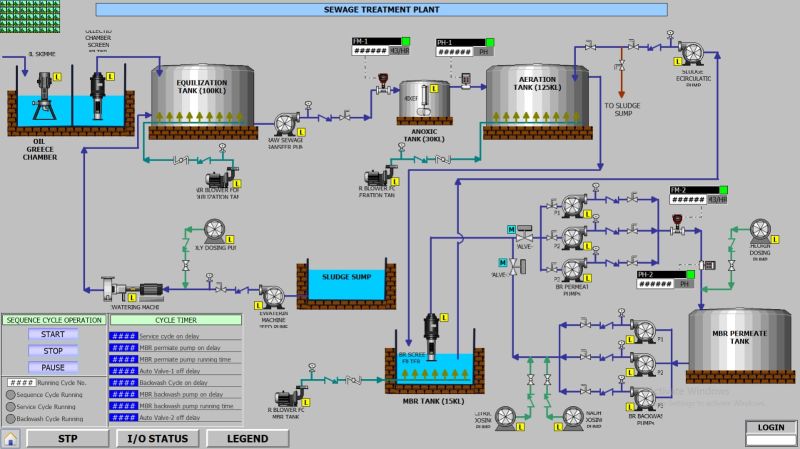
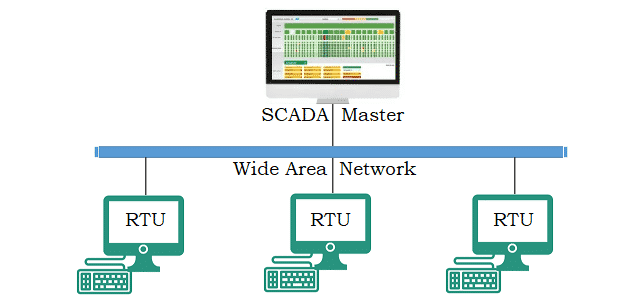
Cybersecurity in SCADA systems are a combination of hardware and software used for industrial automation and control. They collect data from sensors, process it, and enable operators to monitor and control processes in real time. From regulating power grids to managing water supply systems, SCADA systems form the backbone of critical infrastructure.
Key Functions of SCADA Systems:
- Data Acquisition: Collecting real-time data from sensors and field devices.
- Supervisory Control: Allowing operators to make informed decisions and adjustments.
- Alarm Management: Notifying operators of anomalies or potential failures.
- System Monitoring: Offering insights into system performance and health.
Given their critical role, any disruption to SCADA systems can have catastrophic consequences, ranging from operational downtime to public safety risks.